Gallbladder Stones
Gallbladder Stones Treatment in Bangalore
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, are solid deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. These stones develop when components of bile, such as cholesterol or bilirubin, become imbalanced and crystallize. Gallstones vary in size and can range from tiny particles to large stones that can obstruct bile ducts, leading to pain and potential complications.
Dr. Varun Kumar J is a renowned specialist in Bangalore, known for offering advanced laparoscopic techniques for gallbladder stones. Patients benefit from reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times. His extensive experience and patient-centered approach ensure top-quality care, making him the preferred choice for those seeking effective solutions. Dr. Varun Kumar J’s commitment to excellence and personalized treatment plans provide the best gallbladder stone treatment in Bangalore, ensuring optimal outcomes for every patient.
Request A Call Back!!
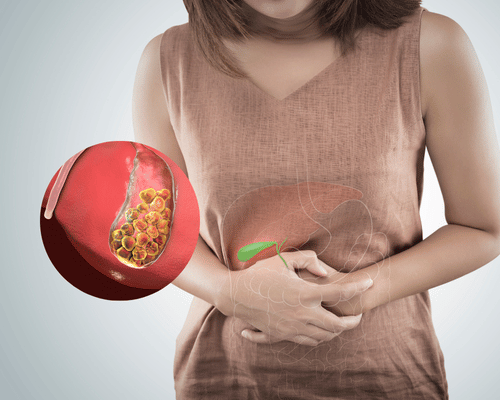
What are Gallbladder Stones?
Gallbladder stones are hard particles that form in the gallbladder from bile components like cholesterol and bilirubin. They can vary in size and can cause pain if they block the bile ducts. Treatment may involve changes in diet, medications to dissolve stones, or surgery to remove the gallbladder if needed
In this blog, we’ll delve into the symptoms, explore various treatment options available, and answer frequently asked questions to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with gallstones may include:
- Pain: Typically in the upper right abdomen, which can be severe and may radiate to the back or shoulder blades.
- Nausea and vomiting: Often accompanied by pain after eating, especially fatty or greasy foods.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes due to bile duct obstruction by a gallstone.
- Fever and chills: Especially if there is inflammation or infection in the gallbladder (cholecystitis).
- Indigestion: Bloating, gas, and discomfort after meals, particularly high-fat meals.
Do You have any of these Gallbladder Stones Symptoms?
Causes
Gallbladder stones, or gallstones, develop when substances in bile—such as cholesterol or bilirubin—become imbalanced and solidify into small, pebble-like formations. Several factors contribute to their formation:
- Excess Cholesterol: When bile contains more cholesterol than bile salts can dissolve, crystals form and eventually harden into stones. This is the most common cause of gallbladder stones.
- Excess Bilirubin: Conditions that increase the breakdown of red blood cells, such as liver cirrhosis or certain blood disorders, can lead to high levels of bilirubin in bile. This excess bilirubin can contribute to the formation of pigment stones.
- Slow Gallbladder Emptying: If the gallbladder does not empty efficiently or there is obstruction in the bile ducts, bile becomes concentrated. This concentration can promote the formation of gallstones over time.
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit genes that predispose them to develop gallstones. The chance of getting gallstones is increased by a family history of the condition.
- Obesity: People who are overweight or obese are at a higher risk of developing gallstones. Obesity can increase cholesterol levels in bile and reduce gallbladder emptying.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly, especially through crash diets or bariatric surgery, can increase the risk of gallstones. Rapid weight loss can alter bile composition and lead to stone formation.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Diseases and conditions that affect the liver and pancreas, such as diabetes, may increase the risk of gallstones.
Types of Gallbladder Stones
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, can be classified into two main types based on their composition and formation:
- Composition: Cholesterol stones are primarily composed of hardened cholesterol. They are yellow-green in color and are the most common type of gallstone, accounting for about 80% of cases.
- Formation: Cholesterol stones form when bile contains too much cholesterol and not enough bile salts or lecithin to dissolve it. They can vary in size from small grains to larger stones.
- Composition: Pigment stones are smaller and darker in color compared to cholesterol stones. They consist of calcium salts and bilirubin.
- Formation: Pigment stones form when there is excess bilirubin in bile. This can occur due to conditions that increase the breakdown of red blood cells, such as liver cirrhosis, hemolytic anemia, or certain infections.
Preventions of Gallbladder Stones
To reduce the risk of developing gallstones, consider the following preventive measures:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for gallstones, so achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial.
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fiber, low in cholesterol and saturated fats, and avoid rapid weight loss diets.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water daily helps maintain proper bile consistency and flow.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
- Limit alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Medical advice: If you have risk factors such as a family history of gallstones or certain medical conditions, consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on prevention strategies.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Stones
Treatment for gallbladder stones depends on their size, composition, symptoms, and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
- Description: If gallstones are small and asymptomatic, your doctor may recommend monitoring without immediate intervention.
- Suitability: This approach is suitable for patients who are not experiencing symptoms and whose gallstones are not causing complications.
- Description: Medications may be prescribed to dissolve cholesterol gallstones, particularly if surgery is not an option or preferred.
- Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA): This medication can help dissolve cholesterol stones over time, but it is most effective for small stones.
- Suitability: Medications are generally suitable for patients with small cholesterol stones who are at a low risk of complications.
- Description: This is the most common surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder, especially if gallstones are causing symptoms or complications.
- Procedure: The surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope (a small, flexible tube with a camera) and specialized surgical tools to remove the gallbladder.
- Advantages: Laparoscopic surgery is minimally invasive, resulting in shorter recovery times and less post-operative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
- Suitability: Recommended for patients with symptomatic gallstones, larger stones, or those at risk of complications like inflammation or infection.
- Description: ERCP combines endoscopy and fluoroscopy to remove stones from the bile ducts.
- Procedure: A flexible tube (endoscope) is passed through the mouth, esophagus, and stomach into the small intestine. A small catheter is then used to remove stones or widen narrowed bile ducts.
- Suitability: ERCP is used when gallstones have moved from the gallbladder into the bile ducts, causing obstruction or complications.
- Description: ESWL uses shock waves to break up gallstones into smaller fragments that can pass through the bile ducts.
- Procedure: The patient lies on a table, and shock waves are delivered externally to the gallbladder to fragment the stones.
- Suitability: ESWL is suitable for patients with smaller stones in the gallbladder who are not candidates for surgery.
- Description: In rare cases where surgery is not possible, a tube (catheter) may be inserted through the skin into the gallbladder to drain bile and relieve symptoms.
- Suitability: Used for patients who are too ill for surgery or have complications that preclude surgical removal of the gallbladder.
- Description: Some individuals may try natural remedies or dietary changes, such as a low-fat diet, to manage symptoms or reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
- Suitability: While these approaches may help manage symptoms or prevent new stones from forming, they are not typically effective for dissolving existing gallstones.
Pre-procedure Care for Gallbladder Stones
Before any procedure, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the treatment plan, benefits, and potential risks.
Doctor may perform blood tests, imaging scans (like ultrasound or CT scan), and other tests to evaluate the size, location, and composition of gallstones.
Doctor will likely advise you to fast for several hours before the procedure. This helps ensure your stomach and intestines are empty, reducing the risk of complications during anesthesia and surgery.
Inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements. Follow their instructions regarding which medications to continue or discontinue before the procedure.
Stay hydrated before the procedure, unless otherwise instructed by your healthcare provider.
Doctor will provide specific instructions on what to expect during and after the procedure, including potential complications and recovery expectations.
Post-procedure Care for Gallbladder Stones
After surgery, you will be monitored in a recovery room until you are fully awake and stable. Vital signs will be monitored to ensure there are no immediate complications.
You may experience some pain or discomfort after surgery. Your healthcare provider will prescribe pain medications or recommend over-the-counter pain relievers to manage this discomfort.
Initially, you may be advised to follow a liquid diet and gradually transition to a regular diet as tolerated. Avoid fatty or greasy foods immediately after surgery.
Rest and avoid strenuous activities for a few days to allow your body to heal. Light activity, such as walking, is encouraged to promote circulation and prevent blood clots.
Keep the incision sites clean and dry. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions on changing dressings and caring for wounds.
Attend follow-up appointments as scheduled to monitor your recovery and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
- Be aware of potential signs of complications, such as fever, increasing pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), or persistent nausea and vomiting. Immediately get in touch with your doctor if you encounter any of these symptoms.
After recovery, your healthcare provider may recommend dietary changes, such as a low-fat diet, and lifestyle adjustments to prevent future gallstone formation and promote overall health.
Myths and Facts of Gallbladder Stones
Myths
- Eating fatty foods directly causes gallbladder stones.
- Only older adults get gallbladder stones.
- Gallbladder stones will dissolve on their own.
- Removing the gallbladder leads to digestive problems.
- Drinking apple cider vinegar can dissolve gallstones.
Facts
- While a high-fat diet can contribute, factors like genetics, obesity, and rapid weight loss also play roles.
- They can occur at any age, though more common in older adults; younger individuals and women can also develop them.
- They typically require treatment; asymptomatic stones may need medical intervention.
- The gallbladder isn't essential for digestion; most people don't have significant issues after surgery.
- No scientific evidence supports this; consult a medical professional for appropriate treatment options.
Looking for Laparoscopic Surgeon for Gallbladder Stones or Treatment for Gallbladder Stones?
Look no further than Dr. Varun Kumar J. he is a reliable and Experienced Gallbladder stones treatment in Bangalore with extensive experience and expertise in Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery, Dr. Varun Kumar J is renowned for his precision and patient-centered care. He specializes in treating gallbladder stones and other gallbladder-related conditions ensuring patients receive top-quality treatment with minimal recovery time.
Dr. Varun Kumar J is dedicated to providing exceptional care and successful outcomes for his patients. His state-of-the-art techniques and commitment to excellence make him a trusted choice for anyone seeking treatment for gallbladder issues in Bangalore. Whether you need surgery for gallstones or other gallbladder problems, Dr. Varun Kumar J is one of the Gallbladder stones Surgeon in Bangalore you can rely on for the best possible.
Conclusion
Gallbladder stones are a common health concern that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards managing their gallbladder health. By staying informed and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges posed by gallbladder stones and maintain their overall well-being. Stay informed about gallbladder stones to protect your health.
Book a Consultation call now!!

FAQs
Diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI are commonly used to visualize gallstones and evaluate the condition of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Untreated gallstones can lead to complications such as inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), blockage of the bile ducts (which can cause pancreatitis or jaundice), or infection.
Not all gallstones cause symptoms or require treatment. Asymptomatic stones may be monitored without intervention, while symptomatic stones may require treatment to relieve symptoms or prevent complications.
Gallstones can interfere with bile flow, which is essential for digesting fats. This can lead to symptoms like bloating, indigestion, and intolerance to fatty foods.
Rapid weight loss can be a risk factor for developing gallstones, but gallbladder stones themselves do not typically cause weight loss as a symptom.
